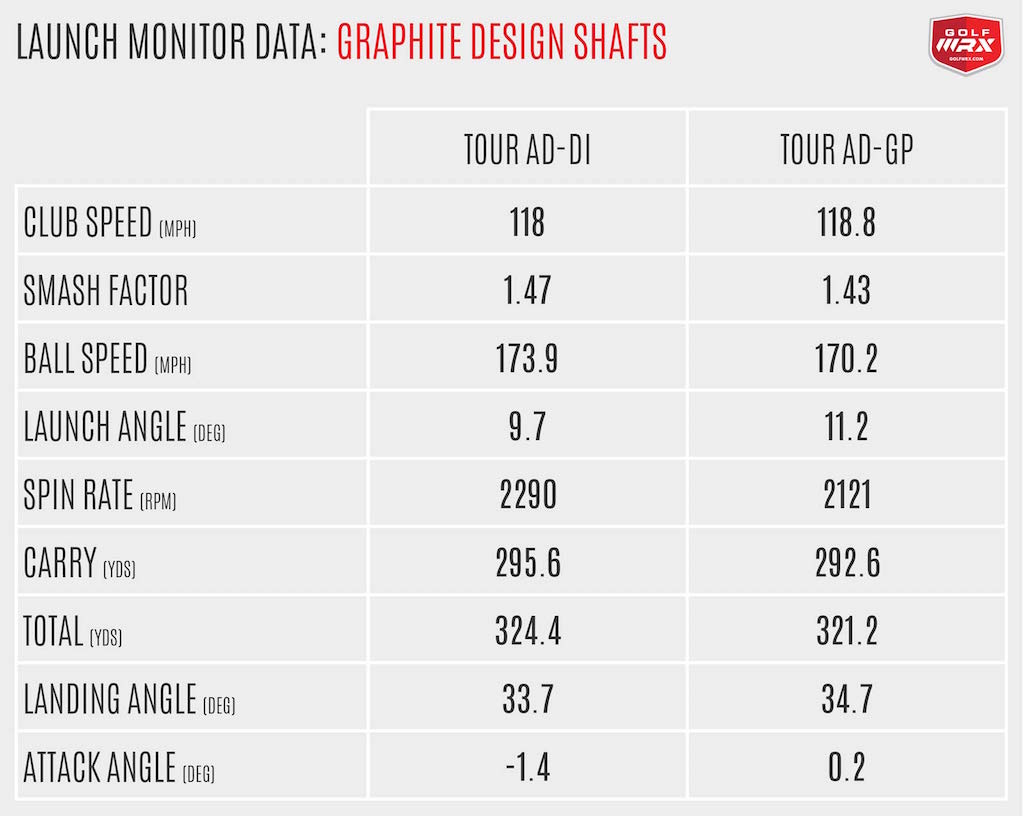
Table Of Content
As you gather more clues (or data), you update your best guess on what's really happening. In terms of applications, besides their heavy usage in medical and pharmaceutical research, Adaptive Designs are also becoming increasingly popular in software testing and market research. In these fields, being able to quickly adjust to early results can give companies a significant advantage. Adaptive Designs are most often seen in clinical trials, particularly in the medical and pharmaceutical fields. Meanwhile, two more classes skip the initial quiz, and then one uses the new method before both take the final quiz. Comparing all four groups will give you a much clearer picture of whether the new teaching method works and whether the pretest itself affects the outcome.
Frequently asked questions about experimental research
If if random assignment of participants to control and treatment groups is impossible, unethical, or highly difficult, consider an observational study instead. You manipulate one or more independent variables and measure their effect on one or more dependent variables. All variables which are not independent variables but could affect the results (DV) of the experiment. At this stage, independent variables are manipulated to study the cause-effect relationship. At this stage, a research question is established that helps to distinguish between dependent and independent variables.
Cluster Randomized Design Cons
In this case, the students are the subjects or dependent variables while the lectures are the independent variables treated on the subjects. Some efficient designs for estimating several main effects were found independently and in near succession by Raj Chandra Bose and K. Kishen in 1940 at the Indian Statistical Institute, but remained little known until the Plackett–Burman designs were published in Biometrika in 1946.
Statistical experiments, following Charles S. Peirce
Inverse relationship between species competitiveness and intraspecific trait variability may enable species coexistence ... - Nature.com
Inverse relationship between species competitiveness and intraspecific trait variability may enable species coexistence ....
Posted: Wed, 03 Apr 2024 07:00:00 GMT [source]
It is used to make predictions and draw conclusions on a subject matter. This is a no equivalent group design example because the samples are not equal. By evaluating the effectiveness of each teacher’s teaching method this way, we may conclude after a post-test has been carried out. Let us consider an academic institution that wants to evaluate the teaching method of 2 teachers to determine which is best. Imagine a case whereby the students assigned to each teacher is carefully selected probably due to personal request by parents or due to stubbornness and smartness. The first two of these groups are tested using the posttest-only method, while the other two are tested using the pretest-posttest method.
Types of experimental research designs
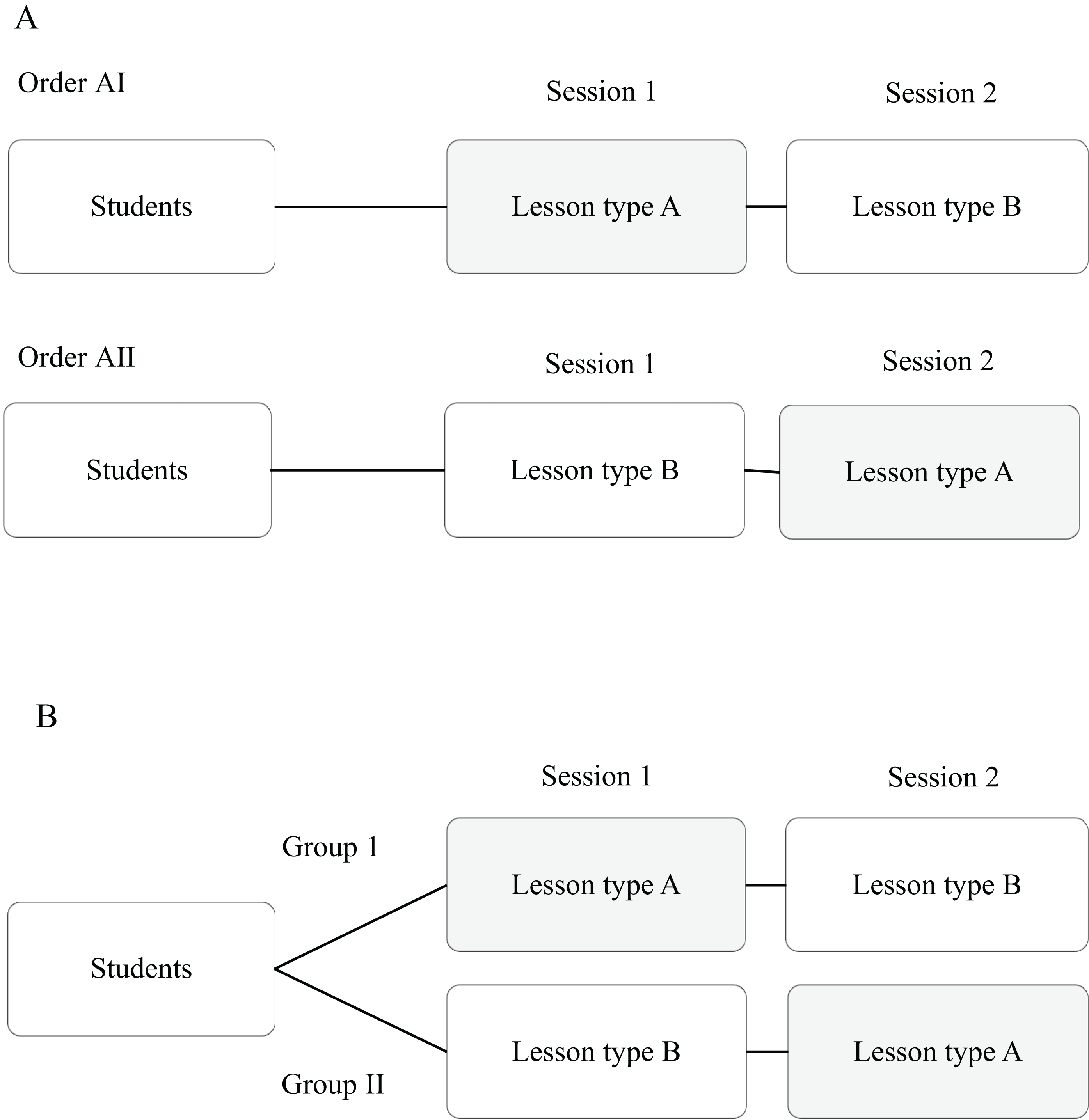
Use of random counterbalancing will result in more random error, but if order effects are likely to be small and the number of conditions is large, this is an option available to researchers. Experimental research contains dependent, independent and extraneous variables. The dependent variables are the variables being treated or manipulated and are sometimes called the subject of the research. Research study design is a framework, or the set of methods and procedures used to collect and analyze data on variables specified in a particular research problem. In a within-subjects design, each participant experiences all conditions, and researchers test the same participants repeatedly for differences between conditions.
Inadequate Literature Study
The statistical design, however, would be a 2 × 3 factorial with independent variables of experience (novice or advanced) and training (isokinetic, isotonic, or isometric) and a dependent variable of strength gain. Note that data were collected according to a 3-factor design but were analyzed according to a 2-factor design and that the dependent variables were different. So a single design statement, usually a statistical design statement, would not communicate which data were collected or how. Readers would be left to figure out on their own how the data were collected.
Between-Subjects Experiments
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A FeaturePaper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook forfuture research directions and describes possible research applications. Experimental research is suitable for research whose goal is to examine cause-effect relationships, e.g. explanatory research. It can be conducted in the laboratory or field settings, depending on the aim of the research that is being carried out. This method is commonly used in engineering and operational research for learning purposes and sometimes as a tool to estimate possible outcomes of real research.
When researching the effect of social interaction on human behavior, the subjects who are placed in 2 different environments are observed throughout the research. No matter the kind of absurd behavior that is exhibited by the subject during this period, its condition will not be changed. The other person is placed in a room with a few other people, enjoying human interaction. There will be a difference in their behaviour at the end of the experiment. Experimental research design can be majorly used in physical sciences, social sciences, education, and psychology.
Pre-Experimental Design
The use of a control group is an important experimental design method that involves having a group of participants that do not receive the treatment or intervention being studied. The control group is used as a baseline to compare the effects of the treatment group. The efficiency of design is essential to gather quantitative data and carrying out statistical analysis during the research process. In this article, we discuss what are experimental design, its importance, and the mistakes to avoid when designing the research structure. In true experimental research, the participants are divided into groups randomly and evenly so as to have an equal distinction. However, in quasi-experimental research, the participants can not be divided equally for ethical or practical reasons.
Your research design must include ways to minimize any risk for your participants and also address the research problem or question at hand. If you cannot manage the ethical norms along with your research study, your research objectives and validity could be questioned. The ultimate goal of a research experiment is to gain valid and sustainable evidence. Therefore, incorrect statistical analysis could affect the quality of any quantitative research. The principle of random allocation is to avoid bias in how the experiment is carried out and limit the effects of participant variables. The variable the experimenter manipulates (i.e., changes) is assumed to have a direct effect on the dependent variable.
This creates a wedge-like pattern over time where more and more participants receive the treatment as the study progresses. It's like rolling out a new policy in phases, monitoring its impact at each stage before extending it to more people. Now let's turn our attention to Covariate Adaptive Randomization, which you can think of as the "matchmaker" of experimental designs. A famous example of this design is the "Little Albert" experiment, conducted by John B. Watson and Rosalie Rayner in 1920. In this study, a young boy was exposed to a white rat and other stimuli several times to see how his emotional responses changed.